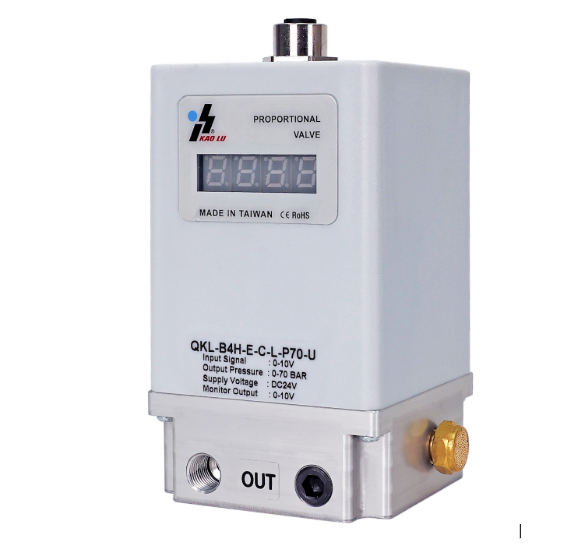
Pressure regulation is crucial in industries that require precision and control. Proportional pressure regulators and electro-pneumatic regulators are two types of devices used in these industries. Both devices control air or gas pressure, but they do so in different ways and are applied in different ways. Knowing these differences helps industries select the right regulator.
Differences between the Proportional Pressure Regulators and Other Types.
A proportional pressure regulator is designed to maintain and control the output that is used. The proportional regulators in these cases do not stagnate but continuously adjust so that the output matches the system.
Key Features:
• Works with electronic or pneumatic control signals
• Automation of flexible peripherals
• Real-time response to systems load
See also: How Oil and Gas Agencies Use Effective Strategies to Reach Their Target Audiences
Methods Used in Electro-Pneumatic Regulators to Achieve Accuracy.
Regulators of this type now shift to unifying electro control signals and pneumatic output. This phenomenon involves converting electrical input to proportional air pressure with the help of controllers and valves.
Ways of working:
1. A PLC or computer sends an electrical signal to the regulator.
2. The circuit board becomes responsible for controlling the signal’s reaction to the incoming pneumatic response.
3. Measurement, along with real-time adjustments to the outcome, is a vital sensor function.
Key Benefits:
• Extreme accuracy in controlling air pressure
• Immediate action in response to changing needs
• Enhanced alignment with contemporary automated systems
Relative Comparison: Proportional Pressure Regulators and Electro Pneumatic Regulators
Responsive Control Inputs Till Ratio Proportional Pressure Electro-Pneumatic Regulators
Regulator Mechanics Electronic or pneumatic, computer- or PLC-controlled electrically.
Mechanics Ratio Regulator Moderates High to Very High
Response Fast Till Ratio Holder Ratio: Slow Responsive Faster and more stable
Used For General automation, robotics, and packaging Medical field, Robotics, Automotive
Automation Ratio Limited Ratio More advanced with digital integration.
Moderate cost: Invest more.
Applications for Proportional Pressure Regulators
Controlling an actuator’s movement and grip strength.
Packaged: Keeping an automated sealer cutting machine stable.
Food & Beverages: Avoiding unhygienic processes by maintaining pressure.
General Manufacturing: for flexible automation lines
Applications for Electro-Pneumatic Regulators
Medical: Ventilators, anesthesia machines, and controlled oxygen supply.
Automotive: automated testing, calibration, and assembly.
Laboratories: precise, low-pressure control for experiments.
Advanced robotics: quick, responsive, precision tasks.
Which control regulators are suitable for your system?
Your industry needs will determine the choice between proportional and electropneumatic regulators.
Choose proportional pressure regulators if:
• You need reliable pressure control at moderate accuracy
• Your application does not need advanced merging integration with PLCs or computers
• Effectiveness from cost is more critical
Choose Electro Pneumatic Regulators if:
• You require ultra-precise control with instantaneous reaction
• Your system is automated and fully integrated with PLCs or computers
• Applications are time-sensitive, such as medical devices or automotive testing
Conclusion:
Both types of devices are critical in industrial automation: Proportional pressure regulators work best in situations where there is a need for flexibility and moderate accuracy is considered, while electropneumatic regulators are used in systems where maximum precision with fast response time is required and advanced systems need to be integrated.
With proper understanding of the situations where each device is to be used, it is also possible to choose the right device in consideration of the cost that will be saved by the long-term reliability, efficiency, and productivity that will be gained.